Overview
In a world where digital payments are becoming the norm, keeping our financial data safe is more critical than ever. Whether you’re shopping online, subscribing to a service, or booking tickets, you’ve likely been asked to enter a three-digit number called CVV2. But what is credit card CVV2 exactly? And why is it important?
In this article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about CVV2 in a simple, realistic way. No fluff. Just straight talk on what CVV2 is, how it works, where you find it, and how it protects you from fraud.
Understanding the Problem
The rise of online shopping has created a new kind of risk: card-not-present fraud. Unlike in-person transactions, where you insert or tap your card, online transactions don’t have that physical presence check. This makes it easier for fraudsters to use stolen card numbers.
Enter CVV2. This small code plays a big role in stopping fraud before it starts.
What Is CVV2 on a Credit Card?
CVV2 stands for “Card Verification Value 2.” It is a three-digit (or sometimes four-digit) security code printed on your credit or debit card. When you’re shopping online or over the phone, the CVV2 is used to verify that you actually have the physical card in hand.
So, if you’re asking, “What is CVV2 on a credit card?” or “What is CVV2 in a credit card?” it’s simply a security feature. It confirms you have the real card, not just the card number.
CVV vs. CVV2 vs. CVC vs. CID: What Do They All Mean?
It can be confusing with all the acronyms. Let’s break them down:
- CVV: Card Verification Value (generic term)
- CVV2: The second generation of CVV, used mostly for online transactions
- CVC: Card Verification Code (used by Mastercard)
- CID: Card Identification Number (used by American Express)
Despite the different names, they all serve the same purpose: confirming that the person making the transaction has the actual card.
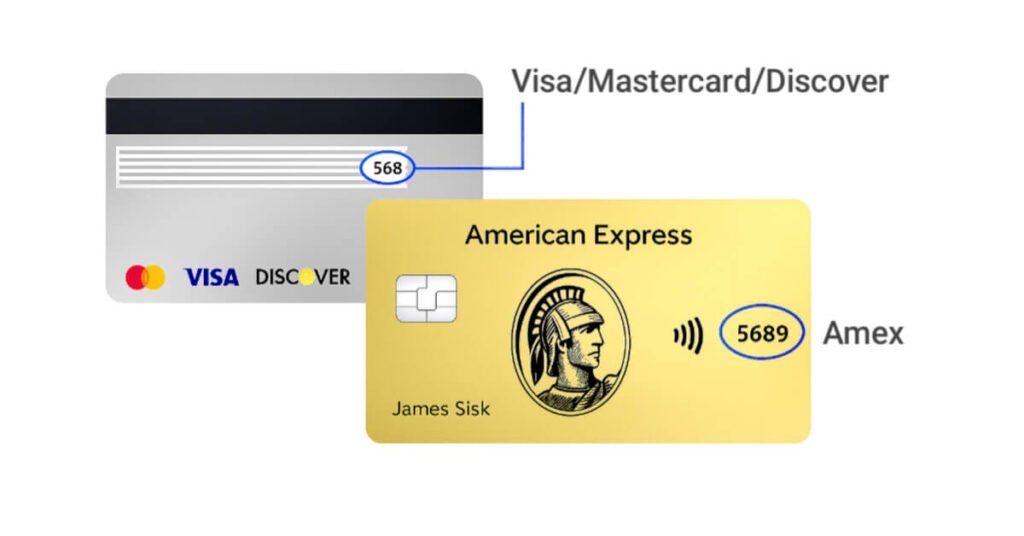
Where to Find the CVV2 on Your Card
- Visa, Mastercard, Discover: Look at the back of your card. The CVV2 is the last three digits in the signature strip.
- American Express: Look at the front. It’s a four-digit code printed just above the card number.
That’s it. No need to decode or guess.
Why CVV2 Matters
When you enter your card number, expiration date, and billing address, you’re providing details that could be stored in online databases. But the CVV2 isn’t supposed to be stored.
That makes it a strong security checkpoint. If someone steals your card number from a hacked database, they still can’t use it online without the CVV2.
In short, the CVV2 acts like a final lock on the door. If you don’t have it, you’re not getting in.
How CVV2 Works in Real Transactions
Here’s what happens behind the scenes:
- You enter your card details and CVV2 during an online checkout.
- The merchant sends your info to the payment processor.
- The processor checks if the CVV2 matches what your bank has on file.
- If it matches, the transaction goes through. If not, it’s declined.
It all happens in seconds. But without that tiny CVV2 check, anyone could use stolen card numbers to shop freely.
How CVV2 Helps Stop Fraud

Let’s say your credit card number is stolen in a data breach. That data alone isn’t enough to make purchases at most legitimate websites. They’ll ask for the CVV2. If the thief doesn’t have it, the payment fails.
While it’s not foolproof (nothing is), CVV2 reduces fraud significantly. It adds a layer of verification that’s hard for criminals to bypass unless they physically have your card.
Best Practices to Protect Your CVV2
Here are some simple, effective tips:
- Don’t share your CVV2 over email, text, or social media.
- Only enter it on secure websites (look for https and the padlock icon).
- Be cautious with phone orders; verify the legitimacy of the business.
- Use a virtual credit card for added security during online purchases.
- Avoid saving card details on websites you don’t fully trust.
Scams Involving CVV2 Codes
Here are some real scenarios to watch out for:
- Phishing Emails: You get a fake email from a bank asking to “verify your card details” including the CVV2.
- Fake Customer Service Calls: Someone claiming to be from your bank asks for the CVV2 over the phone.
- Sketchy Shopping Sites: Fake e-commerce websites ask for CVV2 and then steal your data.
The best way to avoid these scams? Stay alert. Trust your gut. And never share your full card details unless you’re sure it’s safe.
CVV2 and Data Regulations
You might wonder: if CVV2 is so important, can merchants store it?
No. According to the PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), merchants are not allowed to store CVV2 codes after a transaction has been completed. This reduces the risk if the merchant’s system is hacked.
That’s why you often have to re-enter your CVV2 every time you make a purchase. It’s inconvenient but necessary.
Final Thoughts
So, what is credit card CVV2? It’s a simple yet powerful code that protects you during digital transactions. It’s easy to find, easy to use, and makes a big difference in stopping fraud.
Remember the key points:
- CVV2 is a security code on your credit/debit card
- It’s essential for online and phone transactions
- Never share it casually
- Real businesses will never ask for it out of the blue
Use it wisely, protect it carefully, and you’ll be one step ahead in the digital finance game.
FAQs About CVV2
What happens if I enter the wrong CVV2?
The transaction will be declined, and you’ll be asked to try again.
Is CVV2 the same as my PIN?
No. Your PIN is used for ATM and in-person transactions. CVV2 is for online security.
Can I change my CVV2?
No, not directly. If your card is compromised, your bank will issue a new card with a new CVV2.
What if my card doesn’t have a CVV2?
Some older or non-standard cards might not have it. Most modern cards do.
Is it safe to share my CVV with trusted apps?
If the app is legitimate and secure, it’s generally safe. But be cautious.














