Introduction
Imagine a world where your smartwatch alerts your doctor before you feel unwell, a chatbot offers therapy at midnight, and cancer gets diagnosed in seconds. That’s not science fiction—it’s AI in healthcare. In a sector strained by aging populations, rising costs, and physician shortages, artificial intelligence is stepping in not to replace humans, but to empower them. This article explores how AI is solving real healthcare problems today, backed by studies and case examples.
The Problem: Traditional Healthcare Gaps.

Globally, healthcare systems struggle with massive workloads and inefficiencies:
- Doctors often spend more than 50% of their time on paperwork.
- Misdiagnosis contributes to 1 in 10 patient deaths in the U.S. (BMJ, 2020).
- Chronic conditions are rising: 1 in 3 adults has multiple chronic illnesses (CDC).
Manual data handling, late diagnoses, and workforce burnout remain huge issues. There’s also a disconnect between patient behavior and clinical intervention. Traditional systems are reactive, not proactive.
What Happens If We Ignore the Problem?

The consequences are deadly:
- Delays in diagnosis cost lives. A Lancet report (2023) noted over 5 million preventable deaths globally due to diagnostic errors or delays.
- Healthcare access remains unequal, especially in remote or underserved areas.
- Patient data, though abundant, goes underutilized.
Without intervention, systems will collapse under rising demand. This is where AI steps in.
The Solution: AI Applications in Healthcare.

Artificial Intelligence is already transforming many areas of care. Let’s examine seven powerful domains where AI is making a difference:
1. AI in Medical Imaging and Diagnosis.
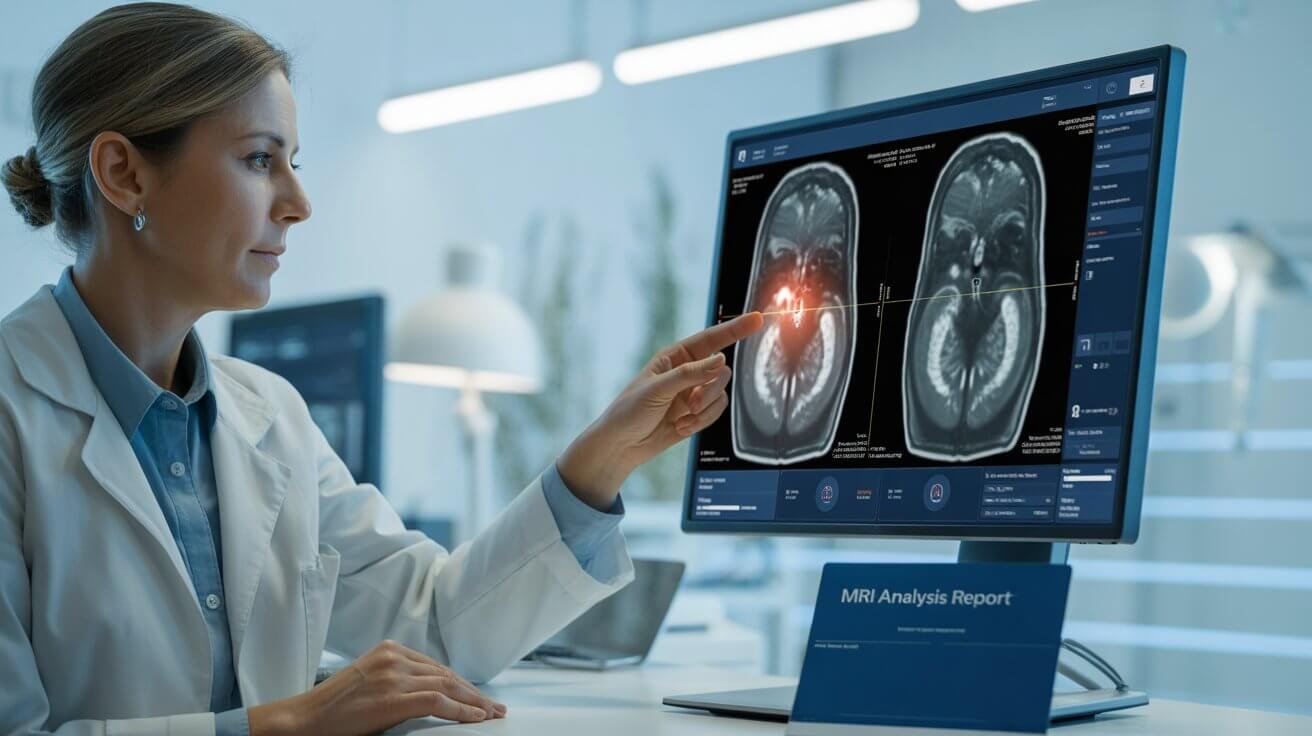
AI models can analyze X-rays, MRIs, and pathology slides faster and more accurately than human experts.
- Example: Google’s DeepMind detects over 50 eye diseases at ophthalmologist-level accuracy.
- PathAI supports cancer detection with a 20% accuracy boost in lab trials.
- Aidoc alerts radiologists in real-time about brain hemorrhages or pulmonary embolisms.
2. Drug Discovery and Development.

AI accelerates the process of finding new drugs.
- Example: Insilico Medicine discovered a fibrosis drug in 18 months, a process that usually takes 5–10 years.
- During COVID-19, BenevolentAI and IBM Watson proposed existing drugs that could be repurposed.
- Machine learning predicts drug success and flags toxicity early, saving billions.
3. Hospital Workflow Automation.
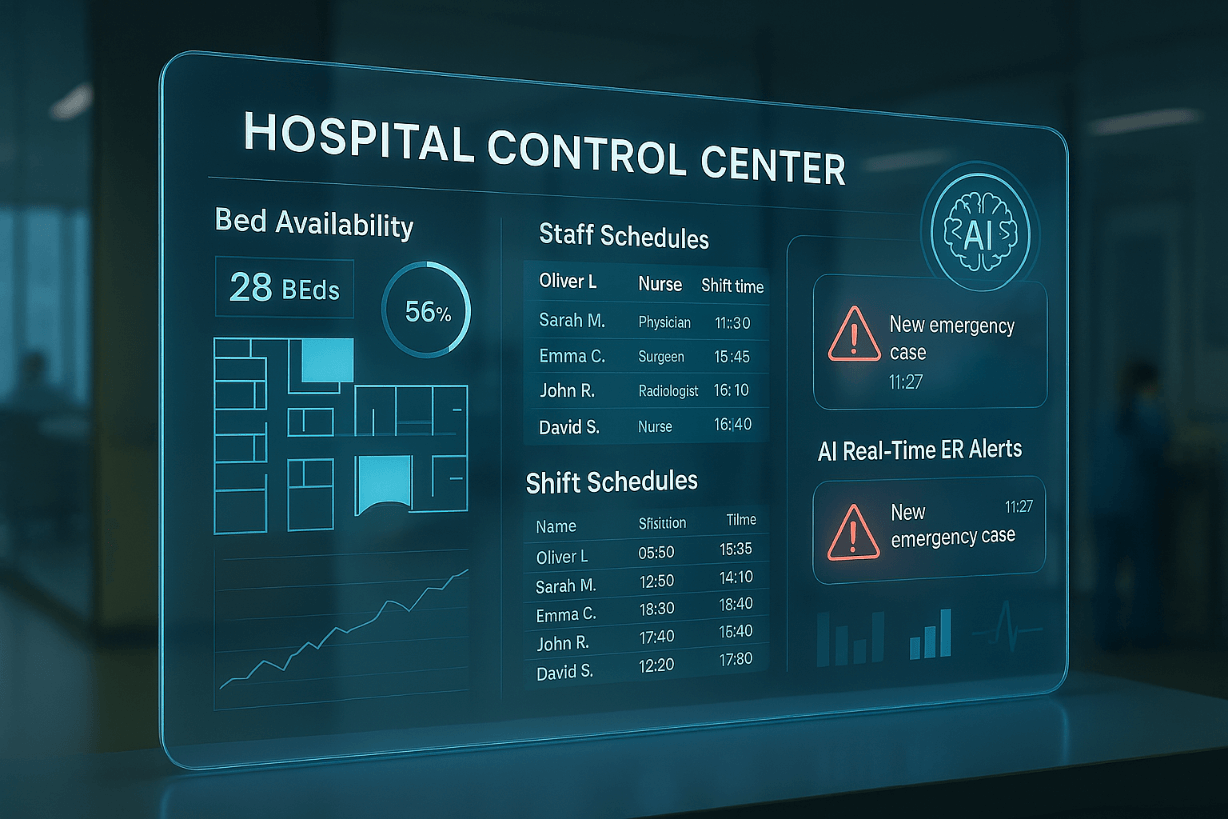
AI helps optimize beds, staff scheduling, and patient flow.
- Mount Sinai’s AI tool analyzed 700,000+ EHRs to predict heart failure 48 hours in advance.
- Qventus AI helps ERs reduce patient wait times by forecasting bottlenecks.
- Cleveland Clinic uses IBM Watson to manage resources more efficiently.
4. Virtual Health Assistants & Symptom Checkers.
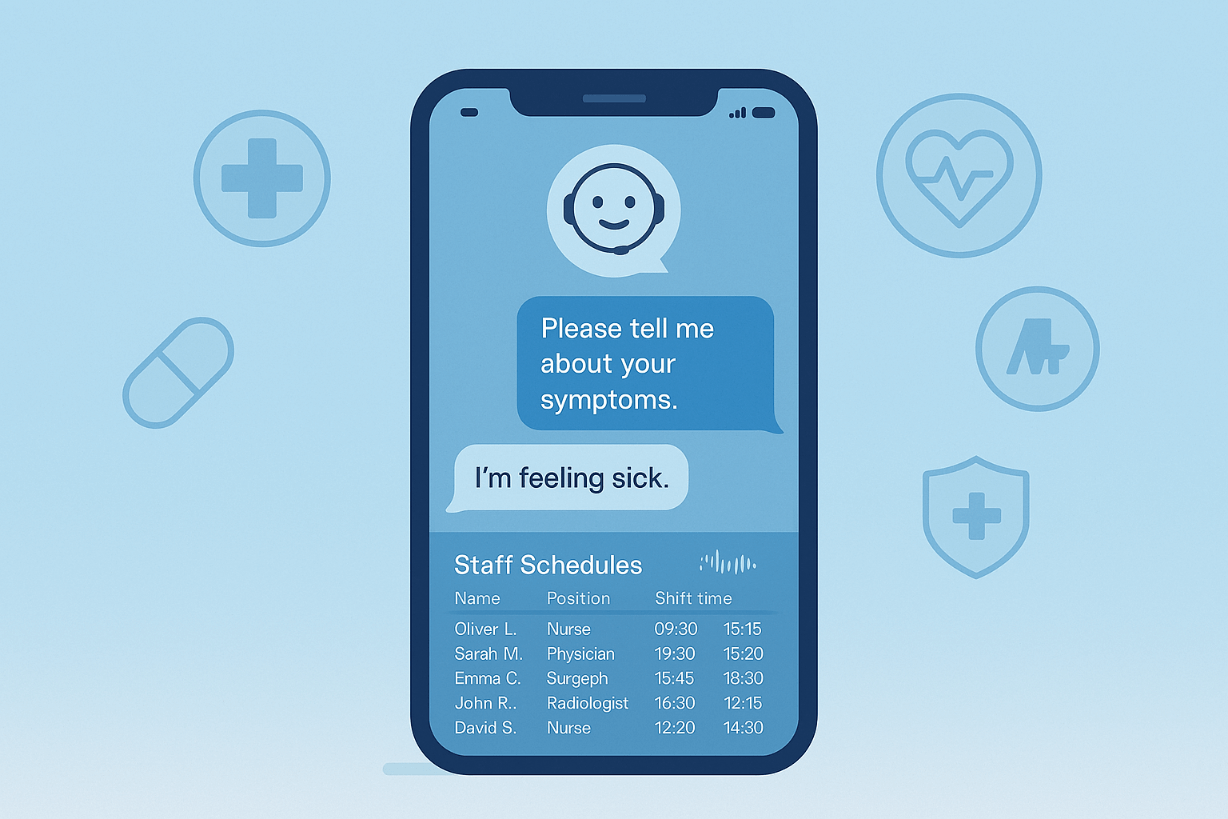
AI-powered apps guide users through health questions and reminders.
- Ada Health performs over 30 million assessments per year.
- Florence (chatbot nurse) reminds users to take meds and track symptoms.
- Sensely uses avatars to offer personalized support to chronic patients.
5. Mental Health and Behavior Monitoring.

AI is filling gaps in therapy access.
- Wysa and Woebot offer cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) 24/7 via AI chat.
- Ginger.io analyzes smartphone usage patterns to detect depression or anxiety early.
- Ellie, a virtual psychologist, interprets facial cues and speech patterns for PTSD.
6. Wearable Devices and Predictive Health Alerts.
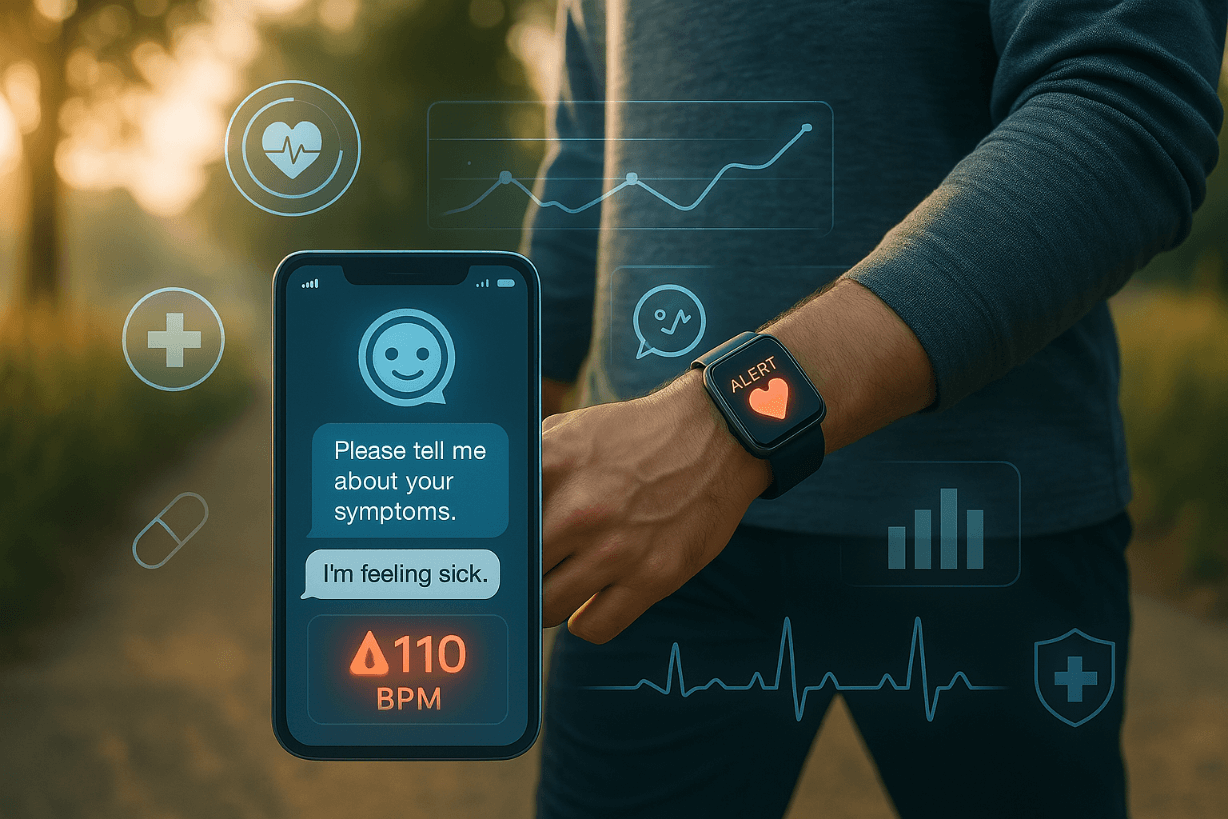
Smart devices generate continuous health data analyzed by AI.
- Apple Watch detects irregular heart rhythms and falls.
- Fitbit + AI can predict flu or sleep disorders based on biometrics.
- Oura Ring has helped detect COVID-19 symptoms 2 days before onset in pilot studies.
7. Robotic and AI-Assisted Surgery.
AI helps perform and guide surgeries.
- Da Vinci Surgical System enables ultra-precise operations through robotic arms.
- ReWalk Robotics builds AI-powered exoskeletons for spinal cord injury rehab.
- Surgical Theater offers VR simulations for brain surgery training.
Summary Table of AI Applications.
| Domain | AI Tools / Approach | Real-World Example | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostics | Image recognition, ML | DeepMind, PathAI, Aidoc | Accuracy and early detection |
| Drug Discovery | Predictive modeling | Insilico, BenevolentAI | Faster development, lower costs |
| Hospital Operations | Predictive analytics, NLP | Mount Sinai, Qventus | Efficiency and cost savings |
| Virtual Assistants | NLP, AI chatbots | Ada Health, Florence | 24/7 support, medication tracking |
| Mental Health | Behavior analysis, speech AI | Woebot, Ellie, Ginger.io | Early support, scalable therapy |
| Wearables | Sensor + ML | Apple Watch, Oura Ring | Preventive care & alerts |
| Surgery & Rehab | Robotics + vision | Da Vinci, ReWalk, Surgical Theater | Precision & rehab enhancement |
Case Studies: AI in Action.
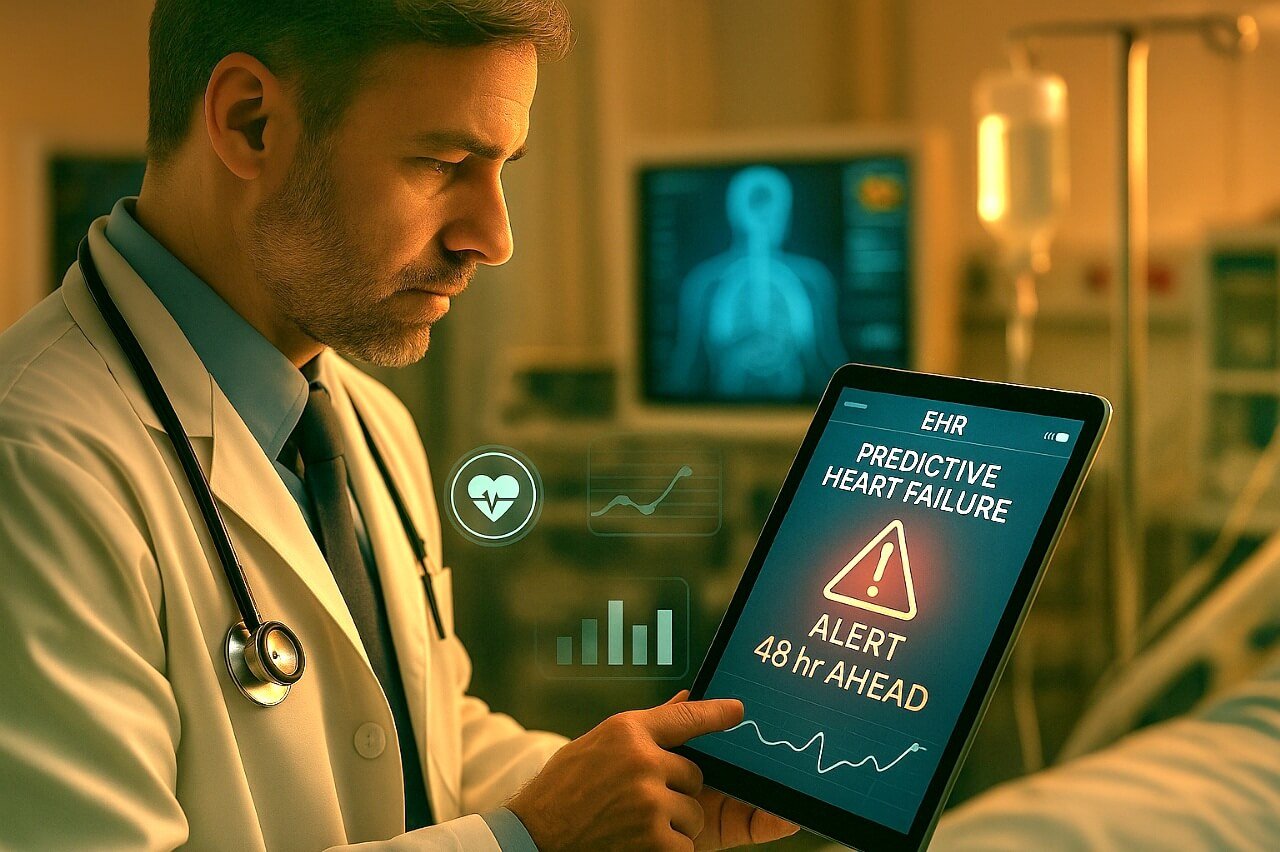

1. Mount Sinai’s Predictive Cardiology
- Tool: AI analyzed 700k+ records
- Outcome: Heart failure predicted 48 hours in advance
- Impact: Faster ICU response and reduced mortality
2. Babylon Health
- Tool: AI chatbot and triage assistant
- Outcome: Reduced patient wait times by 60%
- Reach: Over 1 million consultations per month
3. Butterfly Network
- Tool: Handheld AI ultrasound device
- Impact: Portable diagnostics in remote areas
- Cost: Under $2,000—10x cheaper than traditional ultrasound
Challenges: Why AI Isn’t a Silver Bullet.

- Data Bias: AI can replicate human bias if trained on unbalanced data.
- Explainability: Doctors may not trust AI that they don’t understand.
- Regulation: Few global standards exist for clinical AI tools.
- Privacy: Patient data must be encrypted and anonymized.
- Ethics: Who’s responsible if AI fails—a doctor, developer, or hospital?
Future Outlook: Where AI in Healthcare is Headed.

- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of patients for personalized testing.
- VR + AI: For surgery rehearsal, pain distraction, and physical therapy.
- Genomics + AI: AI-guided DNA analysis for custom treatments.
- AI + Robotics: Autonomous hospital bots for cleaning, transport, and monitoring.
Conclusion

AI isn’t replacing doctors—it’s amplifying their capabilities. It handles repetitive tasks, analyzes more data than any human can, and offers precision that reduces errors. The future of healthcare lies not in man vs. machine but in man + machine. With ethical guardrails and clinician oversight, AI is shaping a more responsive, predictive, and accessible healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
AI in healthcare refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, optimizing hospital operations, and enhancing personalized care.
Can AI replace doctors?
No, AI is a tool to support—not replace—medical professionals. It can analyze data and assist with tasks like image interpretation or scheduling, but clinical judgment and human empathy are irreplaceable.
How accurate is AI in diagnosing diseases?
AI can be highly accurate when trained on large and diverse datasets. Some tools, like those from DeepMind and PathAI, have achieved over 90–95% accuracy in detecting conditions such as eye diseases and cancer in lab settings.
Is AI safe for handling patient data?
Yes, provided the system follows strict data protection regulations like HIPAA or GDPR. AI developers and healthcare providers must ensure data is encrypted, anonymized, and securely stored.
What are some examples of AI tools in healthcare?
Examples include Ada Health (symptom checker), PathAI (cancer detection), Woebot (mental health chatbot), IBM Watson (clinical data analysis), and Apple Watch (health monitoring).
How does AI help in drug development?
AI accelerates drug discovery by analyzing molecular structures, predicting potential reactions, and identifying compounds that may be effective, all of which help reduce the time and cost of bringing drugs to market.
What are the risks of using AI in medicine?
Risks include biased predictions due to poor training data, lack of transparency in how decisions are made (the “black box” problem), regulatory gaps, and ethical concerns around responsibility in case of errors.
Is AI used in mental health care?
Yes. AI chatbots like Wysa and Woebot provide 24/7 emotional support using CBT principles. AI also helps in the early detection of mental health issues by analyzing speech, behavior, and phone usage patterns.
How do wearable devices use AI in healthcare?
Wearables like smartwatches and rings use AI to analyze data from sensors (e.g., heart rate, temperature, oxygen levels) and provide real-time health alerts, helping detect issues like arrhythmias, infections, or sleep disorders.
What is the future of AI in healthcare?
The future includes AI-powered digital twins (personalized virtual models), AI-driven surgery assistants, genomics-based treatment planning, and broader AI use in mental health, rehabilitation, and public health surveillance




